
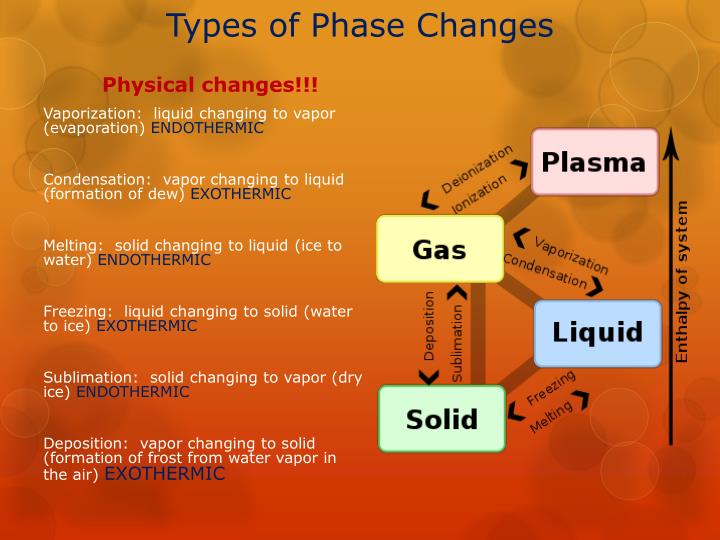
Whenever we are tired off, or we come home after playing in the ground, we feel thirsty, and we come over to the fridge and open the door. Whenever the water droplets in the cloud mix, the cloud becomes heavy to pour down the droplets. Condensation:Ĭondensation is the transformation from which water vapor converts to liquid. This happens when the gaseous substance is cooled. For example: when water vapor (gas) present in the atmosphere changes to a liquid. The process in which the physical state of matter changes from the gaseous state to the liquid state is known as condensation. In reverse, when gas changes to a solid without going into the liquid phase, the process is called deposition or re-sublimation. When a solid changes its state to a gas without going through the liquid phase, the process is called sublimation.
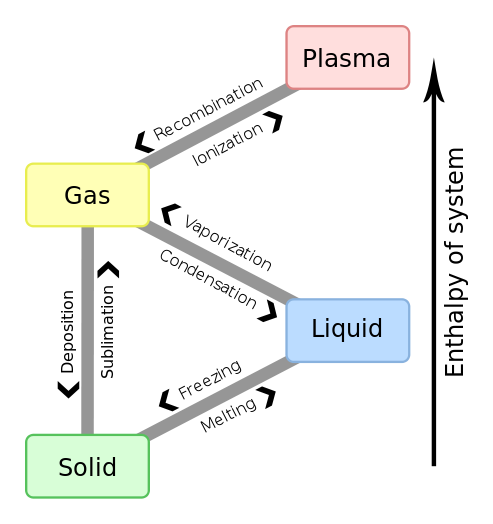
But there are some processes in which solids can be directly converted to gas or gas can be converted to solid. As we generally know, that solid has to get into the liquid phase to reach the gaseous state. Whenever the substances are subjected to certain conditions, change in phases takes place. The six different changes of phases of matter which happens in between the substances are: There are six different phase changes in the states of matter.Ī phase is a distinctive form of a substance, and matter can change among the phases. These changes can take place upon adding some external energies, temperature, and pressure. We all know that matter exists in different forms in our nature. As we know, that matter exists in four states: Solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, but on earth, matter exists in only three states. All matters are made up of tiny particles, such as atoms, molecules or ions. Energy has spontaneously become more dispersed and spread out in that ‘universe’ than when the glass of ice and water was introduced and became a 'system' within it.The matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Matter cannot always be seen. this thermodynamic system, has increased in entropy. This is always true in spontaneous events in a thermodynamic system and it shows the predictive importance of entropy: the final net entropy after such an event is always greater than was the initial entropy.Īs the temperature of the cool water rises to that of the room and the room further cools imperceptibly, the sum of the δQ/T over the continuous range, “at many increments”, in the initially cool to finally warm water can be found by calculus. It is important to realize that the entropy of the surrounding room decreases less than the entropy of the ice and water increases: the room temperature of 298 K is larger than 273 K and therefore the ratio, (entropy change), of δQ/298K for the surroundings is smaller than the ratio (entropy change), of δQ/273K for the ice and water system. The heat δQ for this process is the energy required to change water from the solid state to the liquid state, and is called the enthalpy of fusion, i.e. The entropy of the system, which is δQ/T, increases by δQ/273K.

In this system, some heat ( δQ) from the warmer surroundings at 298 K (25 ☌ 77 ☏) transfers to the cooler system of ice and water at its constant temperature ( T) of 273 K (0 ☌ 32 ☏), the melting temperature of ice. Ice melting provides an example in which entropy increases in a small system, a thermodynamic system consisting of the surroundings (the warm room) and the entity of glass container, ice, water which has been allowed to reach thermodynamic equilibrium at the melting temperature of ice.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
